 

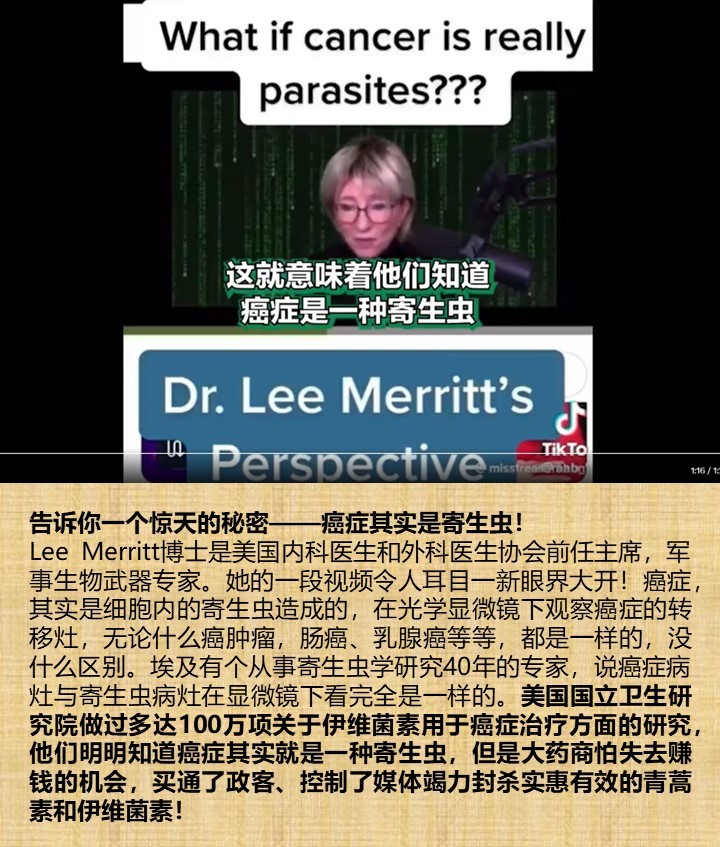









https://www.bitchute.com/video/KY35JseWrU4O/ https://gnews.org/m/1376363?biz=75865469&eu=54368809&t=drgLFmY&gref=






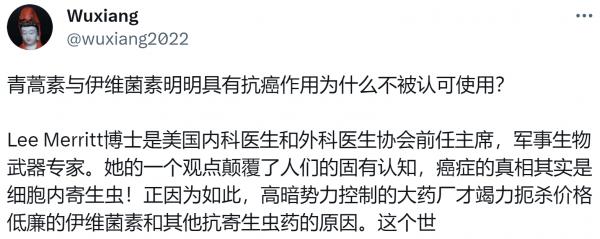
https://twitter.com/wuxiang2022/status/1667668380718088197





2016年12月2日




Infections with eleven species of pathogens associated with cancers are classified as Group 1 carcinogens, definitely “carcinogenic to humans”, by the IARC. These agents include
Helicobacter pylori, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), Opisthorchis viverrini, Clonorchis sinensis, Schistosoma haematobium, human papillomavirus (HPV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), human T-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1), human herpes virus type 8 (HHV-8) and human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)
(Bouvard et al., 2009, IARC, 2012, de Martel et al., 2012). Among parasitic diseases, infections with the two fish-borne liver flukes of the family Opisthorchiidae (trematodes), specifically Opisthorchis viverrini and Clonorchis sinensis, can induce cholangiocarcinoma, and infection with the blood fluke Schistosoma haematobium may cause cancer of the urinary bladder (Bouvard et al., 2009). Although malaria per se is not considered carcinogenic to humans by the IARC, the geographical association between the occurrence of malaria and that of Burkitt lymphoma provides a clue that malaria plays as a co-carcinogenic factor, together with EBV infection, for the development of Burkitt lymphoma (Molyneux et al., 2012). Other species of the genera Opisthorchis and Schistosoma are thought likely to be carcinogenic (Sripa et al., 2007, Pakharukova and Mordvinov, 2016). Intriguingly, Trypanosoma cruzi, the etiological agents of Chagas disease, displays apparently paradoxical roles in malignancy in exerting carcinogenic and anticancer properties (Krementsov, 2009, Sacerdote de et al., 1980). Potential causative roles of other parasitic infections have been postulated (Machicado and Marcos, 2016).
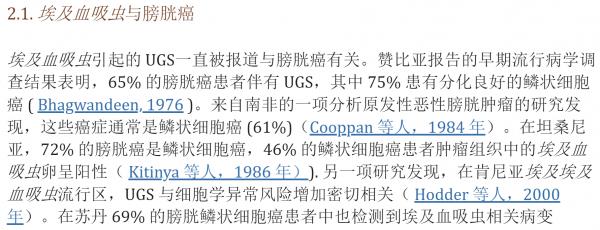
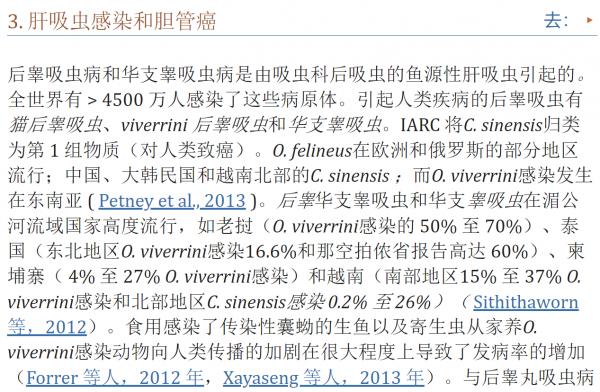
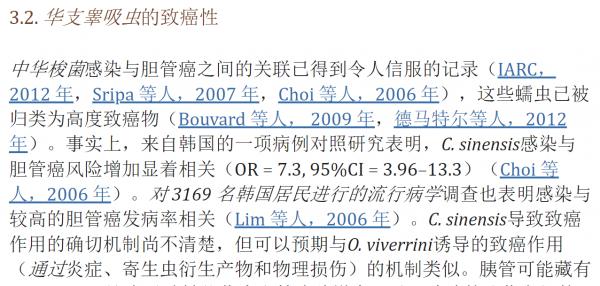
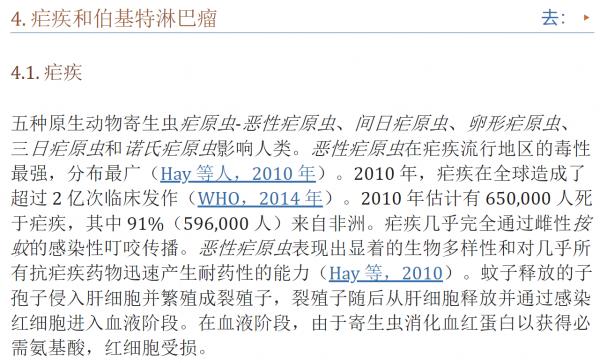
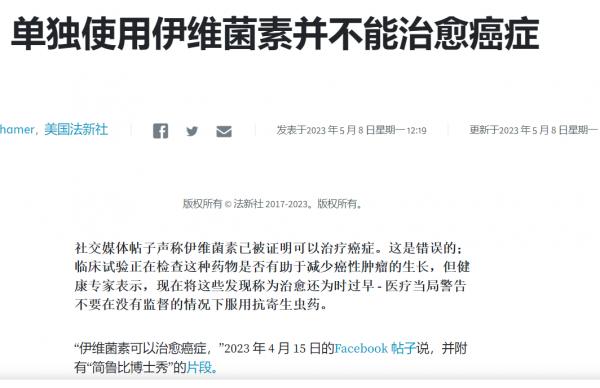
IARC 将与癌症相关的 11 种病原体的感染归类为第 1 组致癌物,绝对是“对人类致癌”。 这些病原体包括幽门螺杆菌、乙型肝炎病毒 (HBV)、丙型肝炎病毒 (HCV)、Opisthorchis viverrini、华支睾吸虫、埃及血吸虫、人乳头瘤病毒 (HPV)、EB 病毒 (EBV)、人类 T 细胞嗜淋巴病毒型 1 (HTLV-1)、8 型人类疱疹病毒 (HHV-8) 和 1 型人类免疫缺陷病毒 (HIV-1)(Bouvard 等人,2009 年;IARC,2012 年;de Martel 等人,2012 年)。 在寄生虫病中,感染后吸虫科(吸虫)的两种鱼源性肝吸虫,特别是后吸虫和华支睾吸虫,可诱发胆管癌,血吸虫血吸虫感染可导致膀胱癌(Bouvard 等人) 等人,2009 年)。 虽然疟疾本身不被 IARC 认为对人类致癌,但疟疾和伯基特淋巴瘤发生之间的地理关联提供了一条线索,即疟疾与 EB 病毒感染一起作为伯基特淋巴瘤发展的共同致癌因素 淋巴瘤(Molyneux 等人,2012 年)。 后睾属和血吸虫属的其他物种被认为可能具有致癌性(Sripa 等人,2007 年;Pakharukova 和 Mordvinov,2016 年)。 有趣的是,恰加斯病的病原体克氏锥虫在恶性肿瘤中表现出明显矛盾的作用,发挥致癌和抗癌特性(Krementsov,2009 年;Sacerdote de 等人,1980 年)。 已经假设了其他寄生虫感染的潜在致病作用(Machicado 和 Marcos,2016 年)。













https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5233816/#:~:text=The%20helminth%20diseases%20schistosomiasis%2C%20opisthorchiasis,both%20carcinogenic%20and%20anticancer%20properties.






http://chrome- extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglcle findmkaj/https://www.cancer.org/cont ent/dam/CRC/PDF/Public/6141.00.pdf

The International Agency for Research on Cancer declared them in 2009 as a Group 1 biological carcinogens in humans. 
































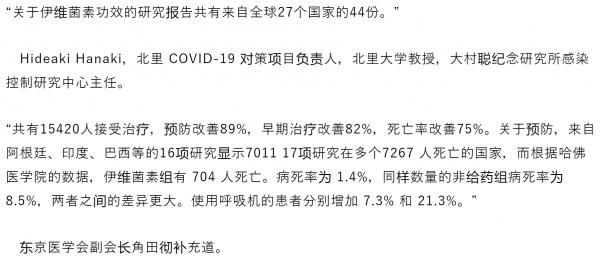

https://www.dailyshincho.jp/article/2021/03211059/?all=1







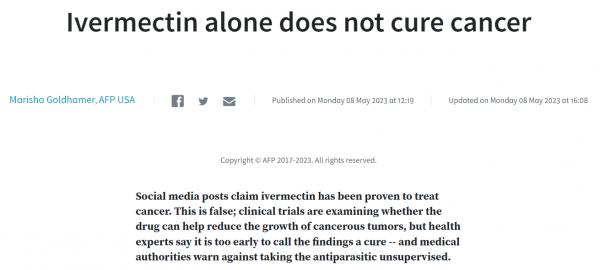










|
